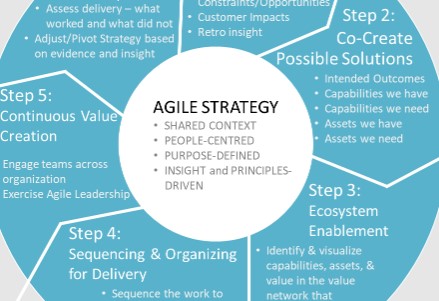
Agile methodologies, traditionally associated with software development, are increasingly recognized as powerful business strategies for growth across various sectors. Applying agile principles beyond IT can foster adaptability, innovation, and customer-centricity, leading to sustainable competitive advantage.
Embracing Iteration and Experimentation
At its core, agile emphasizes iterative development and continuous improvement. In a business context, this translates to launching Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) or small-scale initiatives to test hypotheses and gather real-world feedback. This approach minimizes risk by allowing businesses to learn and adapt quickly based on empirical data, rather than relying solely on extensive planning and assumptions. For example, a marketing team might test different ad campaigns on a small segment of their audience before launching a full-scale promotion.
Cross-Functional Collaboration and Empowerment
Agile promotes cross-functional teams that operate with autonomy and shared responsibility. Breaking down silos and empowering teams to make decisions fosters creativity and accelerates problem-solving. This structure allows businesses to respond more effectively to changing market demands and customer needs. Imagine a product development team that includes members from marketing, sales, and customer service – they can collectively identify opportunities and create solutions tailored to the market, eliminating the delays and miscommunication often associated with traditional hierarchical structures.
Customer-Centricity and Feedback Loops
Agile prioritizes customer satisfaction above all else. By incorporating customer feedback into every stage of the development process, businesses can ensure that their products and services align with market demands. This requires establishing robust feedback loops, actively soliciting customer opinions, and incorporating that input into future iterations. This continuous feedback loop allows businesses to quickly identify and address pain points, refine their offerings, and build stronger customer relationships. Using surveys, focus groups, and analytics to understand customer behavior enables companies to personalize their offerings and create more relevant experiences.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Agile relies heavily on data to inform decisions and track progress. Businesses using agile strategies should establish clear metrics, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and analyze data to identify trends and opportunities. This data-driven approach allows businesses to make informed decisions, optimize their processes, and demonstrate the effectiveness of their agile initiatives. For instance, sales teams can use data to track lead conversion rates, identify high-performing sales channels, and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The business landscape is constantly evolving, and agile organizations must be prepared to adapt. This requires fostering a culture of continuous learning and experimentation, where employees are encouraged to embrace new technologies, explore innovative approaches, and challenge the status quo. Regularly reviewing processes, conducting retrospectives, and seeking external knowledge can help businesses stay ahead of the curve and capitalize on emerging opportunities. This mindset allows companies to pivot quickly when necessary, ensuring long-term sustainability and growth.
By embracing these agile principles, businesses can cultivate a culture of innovation, responsiveness, and customer-centricity, driving sustainable growth and achieving a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market.